|
CVM Class Library
8.1
This C++ class library encapsulates concepts of vector and different matrices including square, band, symmetric and hermitian ones in Euclidean space of real and complex numbers.
|
|
CVM Class Library
8.1
This C++ class library encapsulates concepts of vector and different matrices including square, band, symmetric and hermitian ones in Euclidean space of real and complex numbers.
|
End-user class encapsulating matrix of complex numbers. More...
#include <cvm.h>

Public Member Functions | |
| basic_cmatrix () | |
| Default constructor. | |
| basic_cmatrix (tint nM, tint nN) | |
| Constructor. | |
| basic_cmatrix (TC *pd, tint nM, tint nN) | |
| Constructor. | |
| basic_cmatrix (const TC *pd, tint nM, tint nN) | |
| Constructor. | |
| basic_cmatrix (const basic_cmatrix &m) | |
| Copy constructor. | |
| basic_cmatrix (basic_cmatrix &&m) noexcept | |
| Move constructor. | |
| basic_cmatrix (const CVector &v, bool bBeColumn=true) | |
| Constructor. | |
| basic_cmatrix (const basic_rmatrix< TR > &m, bool bRealPart=true) | |
| Constructor. | |
| basic_cmatrix (const TR *pRe, const TR *pIm, tint nM, tint nN) | |
| Constructor. | |
| basic_cmatrix (const basic_rmatrix< TR > &mRe, const basic_rmatrix< TR > &mIm) | |
| Constructor. | |
| basic_cmatrix (basic_cmatrix &m, tint nRow, tint nCol, tint nHeight, tint nWidth) | |
| Submatrix constructor. | |
| type_proxy< TC, TR > | operator() (tint nRow, tint nCol) throw (cvmexception) |
| Reference to element (l-value) | |
| TC | operator() (tint nRow, tint nCol) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Value of element (not l-value) | |
| CVector | operator() (tint nCol) throw (cvmexception) |
| Column as l-value. | |
| CVector | operator[] (tint nRow) throw (cvmexception) |
| Row as l-value. | |
| const CVector | operator() (tint nCol) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Column as not l-value. | |
| const CVector | operator[] (tint nRow) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Row as not l-value. | |
| CVector | diag (tint nDiag) throw (cvmexception) |
| Diagonal as l-value. | |
| const CVector | diag (tint nDiag) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Diagonal (not l-value) | |
| const basic_rmatrix< TR > | real () const |
| Real part (not l-value) | |
| const basic_rmatrix< TR > | imag () const |
| Imaginary part (not l-value) | |
| basic_cmatrix & | operator= (const basic_cmatrix &m) throw (cvmexception) |
| Assignment operator. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | operator= (basic_cmatrix &&m) throw (cvmexception) |
| Move assignment operator. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | assign (const CVector &v) throw (cvmexception) |
| Vector (as array) assignment. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | assign (const TC *pd) |
| External array assignment. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | assign (tint nRow, tint nCol, const basic_cmatrix &m) throw (cvmexception) |
| Assignment to submatrix. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | set (TC c) |
| Sets all elements to one value. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | assign_real (const basic_rmatrix< TR > &mRe) throw (cvmexception) |
| Assignment to real parts. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | assign_imag (const basic_rmatrix< TR > &mIm) throw (cvmexception) |
| Assignment to imaginary parts. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | set_real (TR d) |
| Sets all real parts to one value. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | set_imag (TR d) |
| Sets all imaginary parts to one value. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | resize (tint nNewM, tint nNewN) throw (cvmexception) |
| Changes dimensions. | |
| bool | operator== (const basic_cmatrix &m) const |
| Matrix comparison. | |
| bool | operator!= (const basic_cmatrix &m) const |
| Matrix comparison. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | operator<< (const basic_cmatrix &m) throw (cvmexception) |
| Matrix replacement. | |
| basic_cmatrix | operator+ (const basic_cmatrix &m) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Addition operator. | |
| basic_cmatrix | operator- (const basic_cmatrix &m) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Subtraction operator. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | sum (const basic_cmatrix &m1, const basic_cmatrix &m2) throw (cvmexception) |
| Sum of matrices. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | diff (const basic_cmatrix &m1, const basic_cmatrix &m2) throw (cvmexception) |
| Difference of matrices. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | operator+= (const basic_cmatrix &m) throw (cvmexception) |
| Increment operator. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | operator-= (const basic_cmatrix &m) throw (cvmexception) |
| Decrement operator. | |
| basic_cmatrix | operator- () const |
| Unary minus operator. | |
| basic_cmatrix | operator* (TR dMult) const |
| Multiply by real number operator. | |
| basic_cmatrix | operator/ (TR dDiv) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Divide by real number operator. | |
| basic_cmatrix | operator* (TC cMult) const |
| Multiply by complex number operator. | |
| basic_cmatrix | operator/ (TC cDiv) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Divide by complex number operator. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | operator*= (TR dMult) |
| Multiply by real number and assign. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | operator/= (TR dDiv) |
| Divide by real number and assign. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | operator*= (TC cMult) |
| Multiply by complex number and assign. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | operator/= (TC cDiv) |
| Divide by complex number and assign. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | normalize () |
| Matrix normalizer. | |
| basic_cmatrix | operator! () const throw (cvmexception) |
| Matrix transposition. | |
| basic_cmatrix | operator~ () const throw (cvmexception) |
| Matrix conjugation. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | transpose (const basic_cmatrix &m) throw (cvmexception) |
| Matrix transposition. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | conj (const basic_cmatrix &m) throw (cvmexception) |
| Matrix conjugation. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | transpose () throw (cvmexception) |
| Matrix transposition (in-place) | |
| basic_cmatrix & | conj () throw (cvmexception) |
| Matrix conjugation (in-place) | |
| CVector | operator* (const CVector &v) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Matrix-vector product. | |
| basic_cmatrix | operator* (const basic_cmatrix &m) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Matrix-matrix product. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | mult (const basic_cmatrix &m1, const basic_cmatrix &m2) throw (cvmexception) |
| Matrix-matrix product. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | rank1update_u (const CVector &vCol, const CVector &vRow) throw (cvmexception) |
| Rank-1 update (unconjugated) | |
| basic_cmatrix & | rank1update_c (const CVector &vCol, const CVector &vRow) throw (cvmexception) |
| Rank-1 update (conjugated) | |
| basic_cmatrix & | swap_rows (tint n1, tint n2) throw (cvmexception) |
| Rows swap. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | swap_cols (tint n1, tint n2) throw (cvmexception) |
| Columns swap. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | solve (const basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mA, const basic_cmatrix &mB, TR &dErr) throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear solver. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | solve_tran (const basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mA, const basic_cmatrix &mB, TR &dErr) throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear solver (transposed) | |
| basic_cmatrix & | solve_conj (const basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mA, const basic_cmatrix &mB, TR &dErr) throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear solver (conjugated) | |
| basic_cmatrix & | solve (const basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mA, const basic_cmatrix &mB) throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear solver. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | solve_tran (const basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mA, const basic_cmatrix &mB) throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear solver (transposed) | |
| basic_cmatrix & | solve_conj (const basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mA, const basic_cmatrix &mB) throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear solver (conjugated) | |
| basic_cmatrix & | solve_lu (const basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mA, const basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mLU, const tint *pPivots, const basic_cmatrix &mB, TR &dErr) throw (cvmexception) |
| LU factorization based linear solver. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | solve_lu (const basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mA, const basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mLU, const tint *pPivots, const basic_cmatrix &mB) throw (cvmexception) |
| LU factorization based linear solver. | |
| RVector | svd () const throw (cvmexception) |
| Singular value decomposition. | |
| RVector | svd (basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mU, basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mVH) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Singular value decomposition. | |
| basic_cmatrix | pinv (TR threshold=basic_cvmMachSp< TR >()) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Pseudo (generalized) inversion. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | pinv (const basic_cmatrix &mA, TR threshold=basic_cvmMachSp< TR >()) throw (cvmexception) |
| Pseudo (generalized) inversion. | |
| basic_cmatrix | gels (bool conjugate, const basic_cmatrix &mB, basic_cvector< TR, TC > &vErr) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Overdetermined or underdetermined linear solver. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | gels (bool conjugate, const basic_cmatrix &mA, const basic_cmatrix &mB, basic_cvector< TR, TC > &vErr) throw (cvmexception) |
| Overdetermined or underdetermined linear solver. | |
| basic_cvector< TR, TC > | gels (bool conjugate, const basic_cvector< TR, TC > &vB, TC &dErr) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Overdetermined or underdetermined linear solver. | |
| basic_cmatrix | gelsy (const basic_cmatrix &mB, tint &rank, TR tol=basic_cvmMachSp< TR >()) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear least squares problem. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | gelsy (const basic_cmatrix &mA, const basic_cmatrix &mB, tint &rank, TR tol=basic_cvmMachSp< TR >()) throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear least squares problem. | |
| basic_cvector< TR, TC > | gelsy (const basic_cvector< TR, TC > &vB, tint &rank, TR tol=basic_cvmMachSp< TR >()) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear least squares problem. | |
| basic_cmatrix | gelss (const basic_cmatrix &mB, basic_rvector< TR > &sv, tint &rank, TR tol=basic_cvmMachSp< TR >()) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear least squares problem. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | gelss (const basic_cmatrix &mA, const basic_cmatrix &mB, basic_rvector< TR > &sv, tint &rank, TR tol=basic_cvmMachSp< TR >()) throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear least squares problem. | |
| basic_cvector< TR, TC > | gelss (const basic_cvector< TR, TC > &vB, basic_rvector< TR > &sv, tint &rank, TR tol=basic_cvmMachSp< TR >()) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear least squares problem. | |
| basic_cmatrix | gelsd (const basic_cmatrix &mB, basic_rvector< TR > &sv, tint &rank, TR tol=basic_cvmMachSp< TR >()) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear least squares problem. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | gelsd (const basic_cmatrix &mA, const basic_cmatrix &mB, basic_rvector< TR > &sv, tint &rank, TR tol=basic_cvmMachSp< TR >()) throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear least squares problem. | |
| basic_cvector< TR, TC > | gelsd (const basic_cvector< TR, TC > &vB, basic_rvector< TR > &sv, tint &rank, TR tol=basic_cvmMachSp< TR >()) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Linear least squares problem. | |
| tint | rank (TR tol=basic_cvmMachSp< TR >()) const throw (cvmexception) |
| Matrix rank. | |
| void | qr (basic_cmatrix< TR, TC > &mQ, basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mR) const throw (cvmexception) |
| QR factorization ("economy" mode) | |
| void | qr (basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mQ, basic_cmatrix< TR, TC > &mR) const throw (cvmexception) |
| QR factorization ("full" mode) | |
| void | lq (basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mL, basic_cmatrix< TR, TC > &mQ) const throw (cvmexception) |
| LQ factorization ("economy" mode) | |
| void | lq (basic_cmatrix< TR, TC > &mL, basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mQ) const throw (cvmexception) |
| LQ factorization ("full" mode) | |
| void | rq (basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mR, basic_cmatrix< TR, TC > &mQ) const throw (cvmexception) |
| RQ factorization ("economy" mode) | |
| void | rq (basic_cmatrix< TR, TC > &mR, basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mQ) const throw (cvmexception) |
| RQ factorization ("full" mode) | |
| void | ql (basic_cmatrix< TR, TC > &mQ, basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mL) const throw (cvmexception) |
| QL factorization ("economy" mode) | |
| void | ql (basic_scmatrix< TR, TC > &mQ, basic_cmatrix< TR, TC > &mL) const throw (cvmexception) |
| QL factorization ("full" mode) | |
| basic_cmatrix & | geru (TC alpha, const CVector &vCol, const CVector &vRow) throw (cvmexception) |
| Rank-1 update matrix-vector operation (unconjugated) | |
| basic_cmatrix & | gerc (TC alpha, const CVector &vCol, const CVector &vRow) throw (cvmexception) |
| Rank-1 update matrix-vector operation (conjugated) | |
| basic_cmatrix & | gemm (const basic_cmatrix &m1, bool bConj1, const basic_cmatrix &m2, bool bConj2, TC cAlpha, TC cBeta) throw (cvmexception) |
| Generic matrix-matrix operation. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | hemm (bool bLeft, const basic_schmatrix< TR, TC > &ms, const basic_cmatrix &m, TC cAlpha, TC cBeta) throw (cvmexception) |
| Generic hermitian matrix-matrix operation. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | vanish () |
| Set matrix to zero. | |
| basic_cmatrix & | randomize_real (TR dFrom, TR dTo) |
| Randomizer (real part) | |
| basic_cmatrix & | randomize_imag (TR dFrom, TR dTo) |
| Randomizer (imaginary part) | |
| TR | norm2 () const override |
| 2-norm | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from Matrix< TR, TC > Public Member Functions inherited from Matrix< TR, TC > | |
| tint | msize () const |
| Number of rows. | |
| tint | nsize () const |
| Number of columns. | |
| tint | ld () const |
| Leading dimension. | |
| tint | rowofmax () const |
| Row with maximum element. | |
| tint | rowofmin () const |
| Row with minimum element. | |
| tint | colofmax () const |
| Column with maximum element. | |
| tint | colofmin () const |
| Column with minimum element. | |
| TR | norm1 () const override |
| 1-norm | |
| TR | norminf () const override |
| Infinity norm. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from basic_array< TR, TC > Public Member Functions inherited from basic_array< TR, TC > | |
| basic_array () | |
| Default constructor. | |
| basic_array (tint nSize, bool bZeroMemory=true) | |
| Constructor. | |
| basic_array (TC *pd, tint nSize, tint nIncr=1) | |
| Constructor. | |
| basic_array (const TC *pd, tint nSize, tint nIncr=1) | |
| Constructor. | |
| basic_array (const TC *begin, const TC *end) | |
| Constructor. | |
| basic_array (const basic_array &a) | |
| Copy constructor. | |
| basic_array (basic_array &&a) noexcept | |
| Move constructor. | |
| basic_array & | operator= (const basic_array &a) throw (cvmexception) |
| Assignment operator. | |
| basic_array & | operator= (basic_array &&a) throw (cvmexception) |
| Move assignment operator. | |
| virtual | ~basic_array () |
| Destructor. | |
| tint | size () const |
| Size (length) of array. | |
| TC * | get () |
| Pointer to data. | |
| const TC * | get () const |
| Const pointer to data. | |
| operator TC * () | |
| Type cast to pointer to data. | |
| operator const TC * () const | |
| Type cast to constant pointer to data. | |
| basic_array & | resize (tint nNewSize) throw (cvmexception) |
| Changes size of array. | |
| tint | incr () const |
| Increment between elements. | |
| tint | indofmax () const |
| Index of element with maximum module. | |
| tint | indofmin () const |
| Index of element with minimum module. | |
| virtual TR | norm () const |
| Euclidean norm. | |
| iterator | begin () |
| (STL) iterator to begin | |
| const_iterator | begin () const |
| (STL) const iterator to begin | |
| iterator | end () |
| (STL) iterator to end | |
| const_iterator | end () const |
| (STL) const iterator to end | |
| reverse_iterator | rbegin () |
| (STL) iterator to begin reversed | |
| const_reverse_iterator | rbegin () const |
| (STL) const iterator to begin reversed | |
| reverse_iterator | rend () |
| (STL) iterator to end reversed | |
| const_reverse_iterator | rend () const |
| (STL) const iterator to end reversed | |
| size_type | max_size () const |
| (STL) maximum possible size of array | |
| size_type | capacity () const |
| (STL) current capacity of array, equal to size() | |
| bool | empty () const |
| (STL) is array empty | |
| reference | front () |
| (STL) reference to first element | |
| const_reference | front () const |
| (STL) const reference to first element | |
| reference | back () |
| (STL) reference to last element | |
| const_reference | back () const |
| (STL) const reference to last element | |
| void | assign (size_type n, const TC &val) throw (cvmexception) |
| (STL) assigns given value to n-th element (0-based) | |
| void | assign (const_iterator begin, const_iterator end) throw (cvmexception) |
| (STL) assigns begin-end iteartor range to array | |
| void | clear () |
| (STL) clears array, dealocates memory and sets size() to zero | |
| void | swap (basic_array &v) throw (cvmexception) |
| (STL) swaps array values, throws cvmexception if sizes are different | |
| reference | at (size_type n) throw (cvmexception) |
| (STL) returns reference to n-th element of array (0-based), throws cvmexception if n is out of boundaries | |
| const_reference | at (size_type n) const throw (cvmexception) |
| (STL) returns const reference to n-th element of array (0-based), throws cvmexception if n is out of boundaries | |
| void | push_back (const TC &x) throw (cvmexception) |
| (STL) pushes new value to the end of array | |
| void | pop_back () throw (cvmexception) |
| (STL) removes last element from array | |
| iterator | insert (iterator position, const TC &x) throw (cvmexception) |
| (STL) inserts element to given position in array | |
| iterator | erase (iterator position) throw (cvmexception) |
| (STL) removes element from given position in array | |
Friends | |
| class | basic_cvector< TR, TC > |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Public Types inherited from basic_array< TR, TC > Public Types inherited from basic_array< TR, TC > | |
| typedef TC | value_type |
| STL-specific value type definition. | |
| typedef value_type * | pointer |
| STL-specific value pointer definition. | |
| typedef value_type * | iterator |
| STL-specific iterator definition. | |
| typedef const value_type * | const_iterator |
| STL-specific const iterator definition. | |
| typedef const value_type * | const_pointer |
| STL-specific const pointer definition. | |
| typedef value_type & | reference |
| STL-specific reference definition. | |
| typedef const value_type & | const_reference |
| STL-specific const reference definition. | |
| typedef size_t | size_type |
| STL-specific size type definition. | |
| typedef ptrdiff_t | difference_type |
| STL-specific difference type definition. | |
| typedef std::reverse_iterator < const_iterator > | const_reverse_iterator |
| STL-specific const reverse iterator definition. | |
| typedef std::reverse_iterator < iterator > | reverse_iterator |
| STL-specific reverse iterator definition. | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from Matrix< TR, TC > Protected Member Functions inherited from Matrix< TR, TC > | |
| Matrix () | |
| Default constructor. | |
| Matrix (tint nM, tint nN, tint nLD, bool bZeroMemory) | |
| Constructor. | |
| Matrix (TC *pd, tint nM, tint nN, tint nLD, tint nSize) | |
| Constructor. | |
| Matrix (const TC *pd, tint nM, tint nN, tint nLD, tint nSize) | |
| Constructor. | |
| Matrix (const BaseArray &v, bool bBeColumn) | |
| Constructor. | |
| Matrix (Matrix &&m) noexcept | |
| Move constructor. | |
| Matrix & | operator= (Matrix &&m) throw (cvmexception) |
| Move assignment operator. | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from Matrix< TR, TC > Protected Attributes inherited from Matrix< TR, TC > | |
| tint | mm |
| Number of rows. | |
| tint | mn |
| Number of columns. | |
| tint | mld |
| Leading dimension. | |
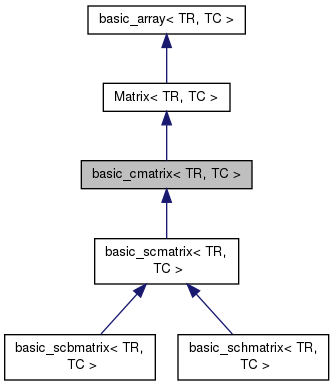
End-user class encapsulating matrix of complex numbers.
TR type stands for treal, TC type stands for tcomplex. Please use predefined cmatrix class in your applications.
|
inline |
Default constructor.
Creates empty matrix. No memory gets allocated.
|
inline |
Constructor.
Creates  cmatrix object where
cmatrix object where 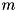 is passed in
is passed in nM parameter (number of rows) and 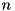 is passed in
is passed in nN (number of columns). Constructor sets all elements to zero. It throws cvmexception in case of non-positive sizes passed or memory allocation failure.
| [in] | nM | Number of rows. |
| [in] | nN | Number of columns. |
|
inline |
Constructor.
Creates  cmatrix object where
cmatrix object where 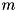 is passed in
is passed in nM parameter (number of rows) and 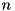 is passed in
is passed in nN (number of columns). It throws cvmexception in case of non-positive sizes passed. Unlike others, this constructor does not allocate memory. It just shares memory with array pointed to by pd (for matrices nIncr=1 is always satisfied).
| [in] | pd | Pointer to array to share memory with. |
| [in] | nM | Number of rows. |
| [in] | nN | Number of columns. |
|
inline |
Constructor.
Creates  cmatrix object where
cmatrix object where 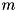 is passed in
is passed in nM parameter (number of rows) and 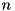 is passed in
is passed in nN (number of columns). Constructor throws cvmexception in case of non-positive sizes passed. This is const version, it allocates memory and copies every element (deep copy) from external array pointed to by pd parameter. It copies nM*nN elements total.
| [in] | pd | Const pointer to external array. |
| [in] | nM | Number of rows. |
| [in] | nN | Number of columns. |
|
inline |
Copy constructor.
Creates cmatrix object as a copy of matrix m. It throws cvmexception in case of memory allocation failure.
| [in] | m | rmatrix to copy from. |
|
inline |
Move constructor.
Implements move semantics introduced in new C++ standard. Moves data ownership from other matrix to newly created object. It's usually executed implicitly in cases like this:
or this
Here temporary result of calling b.operator+(c) will not be destroyed but rather moved to newly created object a.
| [in] | m | rvalue reference to other matrix. |
|
inlineexplicit |
Constructor.
Creates cmatrix object containing v.size() rows and 1 column if bBeColumn is true or 1 row and v.size() columns otherwise. After that it copies elements of vector v to the matrix created. Constructor throws cvmexception in case of memory allocation failure.
| [in] | v | cvector to copy elements from. |
| [in] | bBeColumn | True to create column matrix. |
|
inlineexplicit |
Constructor.
Creates cmatrix object with m.msize() rows and m.nsize() columns and copies matrix m to its real part if bRealPart is true or to its imaginary part otherwise. Constructor throws cvmexception in case of memory allocation failure.
| [in] | m | rmatrix to copy elements from. |
| [in] | bRealPart | true to copy m to real part, false to copy to imaginary part. |
Definition at line 18645 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Constructor.
Creates cmatrix object of size nM by nN and copies every element of arrays pointed to by pRe and pIm to real and imaginary part of the matrix created respectively. Use nullptr pointer to fill up appropriate part with zero values. Constructor throws cvmexception in case of memory allocation failure.
| [in] | pRe | Const pointer to external treal array to copy to real part. |
| [in] | pIm | Const pointer to external treal array to copy to imaginary part. |
| [in] | nM | Number of rows. |
| [in] | nN | Number of columns. |
Definition at line 18695 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Constructor.
Creates cmatrix object of size mRe.msize() by mRe.nsize() (if one of these sizes differs from appropriate size of matrix mIm then constructor throws cvmexception) and copies matrices mRe and mIm to real and imaginary part of the matrix created respectively. Constructor also throws cvmexception in case of memory allocation failure.
Definition at line 18731 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Submatrix constructor.
Creates cmatrix object as submatrix of matrix m. It means that the matrix object created shares memory with some part of m. This part is defined by its upper left corner (parameters nRow and nCol, both are CVM0 based) and its height and width (parameters nHeight and nWidth).
|
inline |
Reference to element (l-value)
Operator provides access to a particular element of calling matrix by its row and column index. Indexes passed are CVM0 based. It returns l-value in order to make possible write access to an element. Operator throws cvmexception if nRow or nCol is outside of boundaries.
Reimplemented in basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 18811 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Value of element (not l-value)
Operator returns value of a particular element of calling matrix by its row and column index. Indexes passed are CVM0 based. Operator throws cvmexception if nRow or nCol is outside of boundaries.
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 18846 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Column as l-value.
Operator provides access to nCol-th column (CVM0 based) of calling matrix by returning cvector sharing memory with it. Operator throws cvmexception if nCol is outside of boundaries.
| [in] | nCol | Index of column (CVM0 based). |
Reimplemented from basic_array< TR, TC >.
Reimplemented in basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 18887 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Row as l-value.
Operator provides access to nRow-th row (CVM0 based) of calling matrix by returning cvector sharing memory with it. Operator throws cvmexception if nRow is outside of boundaries.
| [in] | nRow | Index of row (CVM0 based). |
Reimplemented from basic_array< TR, TC >.
Reimplemented in basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 18927 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Column as not l-value.
Operator creates cvector object as a copy of nCol-th column (CVM0 based) of calling matrix. Operator throws cvmexception if nCol is outside of boundaries.
| [in] | nCol | Index of column (CVM0 based). |
Reimplemented from basic_array< TR, TC >.
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 18958 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Row as not l-value.
Operator creates cvector object as a copy of nRow-th row (CVM0 based) of calling matrix. Operator throws cvmexception if nRow is outside of boundaries.
| [in] | nRow | Index of row (CVM0 based). |
Reimplemented from basic_array< TR, TC >.
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 18990 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Diagonal as l-value.
Operator provides access to nDiag-th diagonal of calling matrix (here nDiag=0 for main diagonal, nDiag<0 for lower diagonals and nDiag>0 for upper ones) by returning cvector sharing memory with it. Operator throws cvmexception if nDiag is outside of boundaries.
| [in] | nDiag | Index of diagonal (0 for main diagonal, negative for lower, positive for upper one). |
Definition at line 19039 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Diagonal (not l-value)
Operator creates cvector object as a copy of nDiag-th diagonal of calling matrix where nDiag=0 for main diagonal, nDiag<0 for lower diagonals and nDiag>0 for upper ones. Operator throws cvmexception if nDiag is outside of boundaries.
| [in] | nDiag | Index of diagonal (0 for main diagonal, negative for lower, positive for upper one). |
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Real part (not l-value)
Creates object of type const rmatrix as real part of calling matrix. Please note that, unlike cvector::real(), this function creates new object not sharing memory with real part of calling matrix, i.e. the matrix returned is not l-value.
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 19104 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Imaginary part (not l-value)
Creates object of type const rmatrix as imaginary part of calling matrix. Please note that, unlike cvector::imag(), this function creates new object not sharing memory with imaginary part of calling matrix, i.e. the matrix returned is not l-value.
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 19135 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Assignment operator.
Sets every element of calling cmatrix to be equal to appropriate element of matrix m and returns reference to the matrix changed. Operator throws cvmexception in case of different matrix dimensions.
| [in] | m | cmatrix to assign from. |
Definition at line 19172 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Move assignment operator.
Implements move semantics introduced in new C++ standard. Moves data ownership from other matrix to calling object. It's usually executed implicitly in cases like this:
Here temporary result of calling b.operator+(c) will not be destroyed but rather moved to calling object a.
| [in] | m | rvalue reference to other matrix. |
Definition at line 19193 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Vector (as array) assignment.
Sets every element of calling matrix to be equal to appropriate element of cvector v as an array. Assignment is performed according to matrix storage (by columns). It's assumed that vector passed is long enough to fill calling matrix. Function throws cvmexception otherwise.
| [in] | v | cvector to assign. |
Reimplemented in basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 19224 of file cvm.h.


|
inline |
External array assignment.
Sets every element of calling matrix to be equal to appropriate element of array pointed to by parameter pd and returns reference to the matrix changed. Assignment is performed according to matrix storage (by columns). It's assumed that array passed is long enough to fill calling matrix.
| [in] | pd | Const pointer to external array. |
Reimplemented from basic_array< TR, TC >.
Reimplemented in basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Assignment to submatrix.
Sets submatrix of calling matrix beginning with row nRow and column nCol to matrix m and returns reference to the matrix changed. Function throws cvmexception if nRow or nCol are not positive or matrix m doesn't fit. Indexes are CVM0 based.
| [in] | nRow | Row index (CVM0 based). |
| [in] | nCol | Column index (CVM0 based). |
| [in] | m | Reference to matrix to assign. |
Definition at line 19292 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Sets all elements to one value.
Sets every element of calling matrix to be equal to parameter c and returns reference to the matrix changed.
| [in] | c | Value to set to. |
Reimplemented from basic_array< TR, TC >.
Reimplemented in basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Assignment to real parts.
Sets real part of every element of calling matrix to value of appropriate element of rmatrix mRe and returns reference to the matrix changed. Function throws cvmexception in case of different sizes of the operands.
| [in] | mRe | rmatrix to assign to real part. |
Definition at line 19352 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Assignment to imaginary parts.
Sets imaginary part of every element of calling matrix to value of appropriate element of rmatrix mIm and returns reference to the matrix changed. Function throws cvmexception in case of different sizes of the operands.
| [in] | mIm | rmatrix to assign to imaginary part. |
Definition at line 19383 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Sets all real parts to one value.
Sets real part of every element of calling matrix to be equal to parameter d and returns reference to the matrix changed.
| [in] | d | Value to set to. |
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Sets all imaginary parts to one value.
Sets imaginary part of every element of calling matrix to be equal to parameter d and returns reference to the matrix changed.
| [in] | d | Value to set to. |
Reimplemented in basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Changes dimensions.
Changes dimensions of calling matrix to to nNewM by nNewN and returns reference to the matrix changed. In case of increasing of its size, the matrix is filled up with zeroes. Function throws cvmexception in case of negative dimension passed or memory allocation failure.
| [in] | nNewM | New number of rows. |
| [in] | nNewN | New number of columns. |
Definition at line 19485 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Matrix comparison.
Operator compares calling matrix with matrix m and returns true if they have same sizes and their appropriate elements differ by not more than cvmMachMin() (the smallest normalized positive number). Returns false otherwise.
| [in] | m | cmatrix to compare to. |
Definition at line 19516 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Matrix comparison.
Operator compares calling matrix with matrix m and returns true if they have different sizes or at least one of their appropriate elements differs by more than cvmMachMin() (the smallest normalized positive number). Returns false otherwise.
| [in] | m | cmatrix to compare to. |
Definition at line 19545 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Matrix replacement.
Destroys calling matrix, creates a new one as a copy of m and returns reference to the matrix changed. Operator throws cvmexception in case of memory allocation failure.
| [in] | m | cmatrix to replace by. |
|
inline |
Addition operator.
Creates object of type cmatrix as sum of calling matrix and matrix m. Operator throws cvmexception in case of different sizes of the operands or memory allocation failure.
| [in] | m | cmatrix to add to calling one. |
Definition at line 19627 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Subtraction operator.
Creates object of type cmatrix as difference of calling matrix and matrix m. It throws cvmexception in case of different sizes of the operands or memory allocation failure.
| [in] | m | cmatrix to subtract from calling one. |
Definition at line 19671 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Sum of matrices.
Assigns sum of matrices m1 and m2 to calling matrix and returns reference to the matrices changed. It throws cvmexception in case of different sizes of the operands.
Definition at line 19717 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Difference of matrices.
Assigns difference of matrices m1 and m2 to calling matrix and returns reference to the matrix changed. It throws cvmexception in case of different sizes of the operands.
Definition at line 19764 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Increment operator.
Adds matrix m to calling matrix and returns reference to the matrix changed. It throws cvmexception in case of different sizes of the operands.
| [in] | m | cmatrix to increment by. |
Definition at line 19811 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Decrement operator.
Subtracts matrix m from calling matrix and returns reference to the matrix changed. It throws cvmexception in case of different sizes of the operands.
| [in] | m | cmatrix to decrement by. |
Definition at line 19856 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Unary minus operator.
Creates object of type cmatrix as calling matrix multiplied by -1. It throws cvmexception in case of memory allocation failure.
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Multiply by real number operator.
Creates object of type cmatrix as product of calling matrix and real number dMult. It throws cvmexception in case of memory allocation failure.
| [in] | dMult | Number to multiply by. |
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Divide by real number operator.
Creates object of type cmatrix as quotient of calling matrix and real number dDiv. It throws cvmexception if dDiv has absolute value equal or less than cvmMachMin() (the smallest normalized positive number). It also throws exception in case of memory allocation failure.
| [in] | dDiv | Number to divide by. |
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Multiply by complex number operator.
Creates object of type cmatrix as product of calling matrix and complex number cMult. It throws cvmexception in case of memory allocation failure.
| [in] | cMult | Number to multiply by. |
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Divide by complex number operator.
Creates object of type cmatrix as quotient of calling matrix and complex number cDiv. It throws cvmexception if cDiv has absolute value equal or less than cvmMachMin() (the smallest normalized positive number). It also throws exception in case of memory allocation failure.
| [in] | cDiv | Number to divide by. |
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Multiply by real number and assign.
Multiplies calling matrix by real number dMult and returns reference to the matrix changed.
| [in] | dMult | Number to multiply by. |
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Divide by real number and assign.
Divides calling matrix by real number dDiv and returns reference to the matrix changed. It throws cvmexception if dDiv has absolute value equal or less than cvmMachMin() (the smallest normalized positive number).
| [in] | dDiv | Number to divide by. |
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Multiply by complex number and assign.
Multiplies calling matrix by complex number cMult and returns reference to the matrix changed.
| [in] | cMult | Number to multiply by. |
Reimplemented in basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Divide by complex number and assign.
Divides calling matrix by complex number cDiv and returns reference to the matrix changed. It throws cvmexception if cDiv has absolute value equal or less than cvmMachMin() (the smallest normalized positive number).
| [in] | cDiv | Number to divide by. |
Reimplemented in basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Matrix normalizer.
Normalizes calling matrix so its Euclidean norm() becomes equal to 1 if it was greater than cvmMachMin() (the smallest normalized positive number) before the call. Does nothing otherwise.
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Matrix transposition.
Creates object of type cmatrix as transposed calling matrix.
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 20222 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Matrix conjugation.
Creates object of type cmatrix as hermitian conjugated calling matrix.
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 20264 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Matrix transposition.
Sets calling matrix to be equal to matrix m transposed. Function throws cvmexception in case of not appropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | m | cmatrix to transpose. |
Definition at line 20309 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Matrix conjugation.
Sets calling matrix to be equal to matrix m conjugated. Function throws cvmexception in case of not appropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | m | cmatrix to conjugate. |
Definition at line 20359 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Matrix transposition (in-place)
Makes calling matrix to be equal to transposed itself. Function throws cvmexception in case of memory allocation failure.
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 20402 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Matrix conjugation (in-place)
Makes calling matrix to be equal to conjugated itself. Function throws cvmexception in case of memory allocation failure.
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 20446 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Matrix-vector product.
Creates object of type cvector as product of calling matrix and vector v. Function throws cvmexception if the number of columns of the calling matrix differs from size of the vector v. Use basic_cvector::mult(const basic_cmatrix<TR,TC>&,const basic_cvector<TR,TC>&) to avoid new object creation.
| [in] | v | cvector to compute product with. |
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 20478 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Matrix-matrix product.
Creates object of type cmatrix as product of calling matrix and matrix m. Operator throws cvmexception if number of columns of calling matrix differs from number of rows of the matrix m. Use mult() to avoid new object creation.
| [in] | m | cmatrix to compute product with. |
Definition at line 20510 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Matrix-matrix product.
Sets calling matrix to be equal to product of matrix m1 by matrix m2 and returns reference to the matrix changed. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
Definition at line 20544 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Rank-1 update (unconjugated)
Sets calling matrix to rank-1 update (unconjugated) of vector vCol and vector vRow. The rank-1 update of vector-column 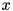 of size
of size 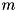 and vector-row
and vector-row 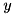 of size
of size 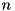 is defined as
is defined as  matrix
matrix
![\[\begin{pmatrix} x_1 y_1 & x_1 y_2 & \cdots & x_1 y_n \\ x_2 y_1 & x_2 y_2 & \cdots & x_2 y_n \\ \hdotsfor{4} \\ x_m y_1 & x_m y_2 & \cdots & x_m y_n \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} x_1 \\ x_2 \\ \vdots \\ x_m \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} y_1 & y_2 & \cdots & y_n \end{pmatrix}.\]](form_28.png)
Function throws cvmexception if number of rows of calling matrix is not equal to vCol.size() or number of columns is not equal to vRow.size().
Definition at line 20593 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Rank-1 update (conjugated)
Sets calling matrix to rank-1 update (conjugated) of vector vCol and vector vRow. The rank-1 update of vector-column 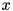 of size
of size 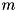 and vector-row
and vector-row 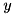 of size
of size 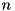 is defined as
is defined as  matrix
matrix
![\[\begin{pmatrix} x_1 y_1^* & x_1 y_2^* & \cdots & x_1 y_n^* \\ x_2 y_1^* & x_2 y_2^* & \cdots & x_2 y_n^* \\ \hdotsfor{4} \\ x_m y_1^* & x_m y_2^* & \cdots & x_m y_n^* \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} x_1 \\ x_2 \\ \vdots \\ x_m \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} y_1^* & y_2^* & \hdots & y_n^* \end{pmatrix},\]](form_65.png)
where 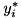 is
is 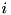 -th complex conjugated element of
-th complex conjugated element of 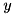 . Function throws cvmexception if number of rows of calling matrix is not equal to
. Function throws cvmexception if number of rows of calling matrix is not equal to vCol.size() or number of columns is not equal to vRow.size().
Definition at line 20648 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Rows swap.
Swaps two rows of calling matrix and returns reference to the matrix changed. n1 and n2 are indexes of rows to be swapped, both are CVM0 based. Function throws cvmexception if one of the parameters is outside of boundaries.
| [in] | n1 | Row index to swap. |
| [in] | n2 | Row index to swap. |
Reimplemented in basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Columns swap.
Swaps two columnss of calling matrix and returns reference to the matrix changed. n1 and n2 are indexes of columns to be swapped, both are CVM0 based. Function throws cvmexception if one of the parameters is outside of boundaries.
| [in] | n1 | Column index to swap. |
| [in] | n2 | Column index to swap. |
Reimplemented in basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Linear solver.
Sets calling matrix to be equal to solution 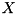 of matrix linear equation
of matrix linear equation 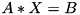 where parameter
where parameter mA is square complex matrix  and parameter
and parameter mB is complex matrix  . Function returns reference to the matrix changed. It also sets output parameter
. Function returns reference to the matrix changed. It also sets output parameter dErr to be equal to the norm of computation error. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands or when the matrix  is close to singular.
is close to singular.
|
inline |
Linear solver (transposed)
Sets calling matrix to be equal to solution 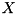 of matrix linear equation
of matrix linear equation 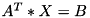 (which is equivalent to
(which is equivalent to 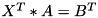 ) where parameter
) where parameter mA is square complex matrix  and parameter
and parameter mB is complex matrix  . Function returns reference to the matrix changed. It also sets output parameter
. Function returns reference to the matrix changed. It also sets output parameter dErr to be equal to the norm of computation error. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands or when the matrix  is close to singular.
is close to singular.
|
inline |
Linear solver (conjugated)
Sets calling matrix to be equal to solution 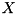 of matrix linear equation
of matrix linear equation 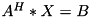 (which is equivalent to
(which is equivalent to 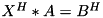 ) where parameter
) where parameter mA is square complex matrix  and parameter
and parameter mB is complex matrix  . Function returns reference to the matrix changed. It also sets output parameter
. Function returns reference to the matrix changed. It also sets output parameter dErr to be equal to the norm of computation error. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands or when the matrix  is close to singular.
is close to singular.
|
inline |
Linear solver.
Sets calling matrix to be equal to solution 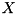 of matrix linear equation
of matrix linear equation 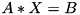 where parameter
where parameter mA is square complex matrix  and parameter
and parameter mB is complex matrix  . Function returns reference to the matrix changed. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands or when the matrix
. Function returns reference to the matrix changed. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands or when the matrix  is close to singular.
is close to singular.
Definition at line 20908 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Linear solver (transposed)
Sets calling matrix to be equal to solution 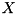 of matrix linear equation
of matrix linear equation 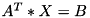 (which is equivalent to
(which is equivalent to 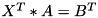 ) where parameter
) where parameter mA is square complex matrix  and parameter
and parameter mB is complex matrix  . Function returns reference to the matrix changed. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands or when the matrix
. Function returns reference to the matrix changed. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands or when the matrix  is close to singular.
is close to singular.
Definition at line 20955 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Linear solver (conjugated)
Sets calling matrix to be equal to solution 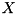 of matrix linear equation
of matrix linear equation 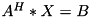 (which is equivalent to
(which is equivalent to 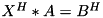 ) where parameter
) where parameter mA is square complex matrix  and parameter
and parameter mB is complex matrix  . Function returns reference to the matrix changed. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands or when the matrix
. Function returns reference to the matrix changed. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands or when the matrix  is close to singular.
is close to singular.
Definition at line 21002 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
LU factorization based linear solver.
Sets calling matrix to be equal to solution 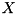 of matrix linear equation
of matrix linear equation 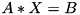 where parameter
where parameter mA is square complex matrix  , parameter
, parameter mLU is LU factorization (see srmatrix::low_up() ) of matrix  , parameter
, parameter pPivots is an array of pivot numbers created while factorizing matrix  and parameter
and parameter mB is complex matrix  . Function returns reference to the matrix changed. It also sets output parameter
. Function returns reference to the matrix changed. It also sets output parameter dErr to be equal to the norm of computation error. This function is useful when you need to solve few linear equations of kind 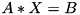 with the same matrix
with the same matrix  and different matrices
and different matrices  . In such case you save on matrix
. In such case you save on matrix  factorization since it's needed to be performed just one time. Throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the objects or when matrix
factorization since it's needed to be performed just one time. Throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the objects or when matrix  is close to singular.
is close to singular.
| [in] | mA | scmatrix  . . |
| [in] | mLU | LU factorization of matrix  . . |
| [in] | pPivots | pivots vector. |
| [in] | mB | cmatrix  . . |
| [out] | dErr | Norm of computation error. |
Definition at line 21077 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
LU factorization based linear solver.
Sets calling matrix to be equal to solution 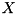 of matrix linear equation
of matrix linear equation 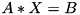 where parameter
where parameter mA is square complex matrix  , parameter
, parameter mLU is LU factorization (see srmatrix::low_up() ) of matrix  , parameter
, parameter pPivots is an array of pivot numbers created while factorizing matrix  and parameter
and parameter mB is complex matrix  . Function returns reference to the matrix changed. This function is useful when you need to solve few linear equations of kind
. Function returns reference to the matrix changed. This function is useful when you need to solve few linear equations of kind 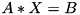 with the same matrix
with the same matrix  and different matrices
and different matrices  . In such case you save on matrix
. In such case you save on matrix  factorization since it's needed to be performed just one time. Throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the objects or when matrix
factorization since it's needed to be performed just one time. Throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the objects or when matrix  is close to singular.
is close to singular.
| [in] | mA | scmatrix  . . |
| [in] | mLU | LU factorization of matrix  . . |
| [in] | pPivots | pivots vector. |
| [in] | mB | cmatrix  . . |
Definition at line 21154 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Singular value decomposition.
Creates rvector of singular values
![\[ \sigma_1\ge\sigma_2\ge\dots\ge\sigma_{\min(m,n)}\ge 0 \]](form_44.png)
of  complex matrix
complex matrix  (calling matrix). These values are the main diagonal of matrix
(calling matrix). These values are the main diagonal of matrix 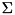 of the singular value decomposition
of the singular value decomposition
![\[ A=U\Sigma V^H \]](form_46.png)
where 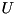 and
and 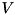 are orthogonal for real
are orthogonal for real  and unitary for complex
and unitary for complex  .
. 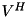 is transposed
is transposed 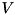 for real one and hermitian conjugated
for real one and hermitian conjugated 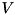 for complex one. First
for complex one. First 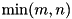 columns of matrices
columns of matrices 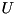 and
and 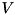 are left and right singular vectors of
are left and right singular vectors of  respectively. Singular values and singular vectors satisfy
respectively. Singular values and singular vectors satisfy
![\[ Av_i=\sigma_i u_i\ \ \text{ and }\ \ A^Hu_i=\sigma_i v_i \]](form_51.png)
where 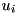 and
and 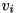 are
are 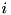 -th columns of
-th columns of 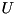 and
and 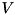 respectively. Function throws cvmexception in case of convergence error.
respectively. Function throws cvmexception in case of convergence error.
Definition at line 21227 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Singular value decomposition.
Creates rvector of singular values
![\[ \sigma_1\ge\sigma_2\ge\dots\ge\sigma_{\min(m,n)}\ge 0 \]](form_44.png)
of  complex matrix
complex matrix  (calling matrix). These values are the main diagonal of matrix
(calling matrix). These values are the main diagonal of matrix 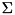 of the singular value decomposition
of the singular value decomposition
![\[ A=U\Sigma V^H \]](form_46.png)
where 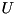 and
and 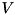 are orthogonal for real
are orthogonal for real  and unitary for complex
and unitary for complex  .
. 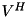 is transposed
is transposed 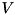 for real one and hermitian conjugated
for real one and hermitian conjugated 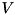 for complex one. First
for complex one. First 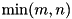 columns of matrices
columns of matrices 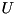 and
and 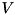 are left and right singular vectors of
are left and right singular vectors of  respectively. Singular values and singular vectors satisfy
respectively. Singular values and singular vectors satisfy
![\[ Av_i=\sigma_i u_i\ \ \text{ and }\ \ A^Hu_i=\sigma_i v_i \]](form_51.png)
where 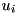 and
and 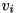 are
are 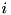 -th columns of
-th columns of 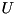 and
and 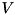 respectively. Function sets output parameter
respectively. Function sets output parameter mU to be equal to square matrix 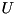 of size
of size 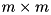 and
and mVH to be equal to square matrix 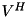 of size
of size 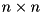 . Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate calling object size (it must be equal to
. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate calling object size (it must be equal to 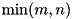 ), matrix
), matrix mU size (must be 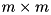 ), matrix
), matrix mVH size (must be  ) or in case of convergence error.
) or in case of convergence error.
Definition at line 21305 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Pseudo (generalized) inversion.
Creates object of type cmatrix as pseudo inverted calling matrix. Matrix pseudo inversion (aka Moore-Penrose generalized inversion) definition: 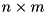 matrix
matrix 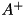 is pseudo inversion of
is pseudo inversion of  matrix
matrix  if the following two equations are satisfied:
if the following two equations are satisfied:
![\[ AA^{+}A=A,\\ A^{+}=QA^H=A^HP \]](form_128.png)
where 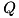 and
and 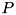 are some matrices. To compute the pseudo inversion, we use singular value decomposition
are some matrices. To compute the pseudo inversion, we use singular value decomposition
![\[ A = U\Sigma V^H \]](form_83.png)
of matrix  , thus
, thus
![\[ A^{+} = V\Sigma^{-1}U^{H}, \]](form_84.png)
where 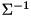 is diagonal
is diagonal 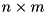 matrix having inverted diagonal values of matrix
matrix having inverted diagonal values of matrix  if they are greater than some threshold, and zeros otherwise. The
if they are greater than some threshold, and zeros otherwise. The threshold parameter sets minimum distinguishable from zero singular value to be used to compute the pseudo inversion. All values equal or less than the threshold are treated as zeros. Function throws cvmexception in case of memory allocation failure.
| [in] | threshold | Algorithm threshold. |
Definition at line 21368 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Pseudo (generalized) inversion.
Sets calling matrix to be equal to complex matrix mA pseudo inverted. Matrix pseudo inversion (aka Moore-Penrose generalized inversion) definition: 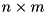 matrix
matrix 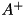 is pseudo inversion of
is pseudo inversion of  matrix
matrix  if the following two equations are satisfied:
if the following two equations are satisfied:
![\[ AA^{+}A=A,\\ A^{+}=QA^H=A^HP \]](form_128.png)
where 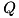 and
and 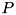 are some matrices. To compute the pseudo inversion, we use singular value decomposition
are some matrices. To compute the pseudo inversion, we use singular value decomposition
![\[ A = U\Sigma V^H \]](form_83.png)
of matrix  , thus
, thus
![\[ A^{+} = V\Sigma^{-1}U^{H}, \]](form_84.png)
where 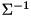 is diagonal
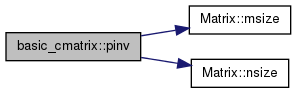
is diagonal 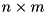 matrix having inverted diagonal values of matrix
matrix having inverted diagonal values of matrix  if they are greater than some threshold, and zeros otherwise. The
if they are greater than some threshold, and zeros otherwise. The threshold parameter sets minimum distinguishable from zero singular value to be used to compute the pseudo inversion. All values equal or less than the threshold are treated as zeros. Function throws cvmexception in case of not appropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | mA | Matrix to pseudo invert. |
| [in] | threshold | Algorithm threshold. |
Definition at line 21432 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Overdetermined or underdetermined linear solver.
Creates object of type cmatrix as a solution of overdetermined or underdetermined linear systems
![\[ A*x=b \]](form_34.png)
for  complex matrix
complex matrix  (or its conjugated one) where
(or its conjugated one) where  is a vector of length
is a vector of length 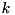 combined to
combined to
![\[ A*X=B \]](form_86.png)
for multiple vectors  stored as columns of
stored as columns of 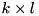 matrix
matrix  where
where 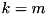 in non-conjugated case and
in non-conjugated case and 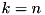 otherwise. The algorithm uses QR or LQ factorization of
otherwise. The algorithm uses QR or LQ factorization of  . It is assumed that
. It is assumed that  has full rank, infinity returned otherwise. Internally function uses
has full rank, infinity returned otherwise. Internally function uses ZGELS LAPACK routines. If 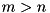 and
and conjugate=false or 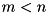 and
and conjugate=true, then the system is overdetermined, thus the algorithm tries to find the least squares solution 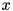 of the problem
of the problem
![\[ \|A*x-b\|_2\to\min\quad\text{or}\quad\|A^H*x-b\|_2\to\min\ \]](form_40.png)
respectively. Real number dErr (or vector vErr for multiple vector  case) returns residual sum of squares. The system is underdetermined otherwise, and the algorithm finds its minimum norm solution. In this case
case) returns residual sum of squares. The system is underdetermined otherwise, and the algorithm finds its minimum norm solution. In this case bErr is set to zero. In both cases the solution computed satisfies  , but this algorithm is faster than pseudo inversion. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
, but this algorithm is faster than pseudo inversion. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | conjugate | True to compute for transposed matrix  (calling matrix). (calling matrix). |
| [in] | mB | cmatrix  . . |
| [out] | vErr | Norms of computation errors. |
Definition at line 21508 of file cvm.h.
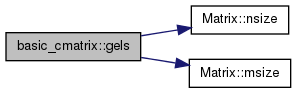
|
inline |
Overdetermined or underdetermined linear solver.
Sets calling matrix to a solution of overdetermined or underdetermined linear systems
![\[ A*x=b \]](form_34.png)
for  complex matrix
complex matrix  (or conjuated one, parameter
(or conjuated one, parameter mA) where  is a vector of length
is a vector of length 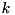 combined to
combined to
![\[ A*X=B \]](form_86.png)
for multiple vectors  stored as columns of
stored as columns of 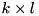 matrix
matrix  where
where 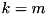 in non-conjugated case and
in non-conjugated case and 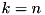 otherwise. The algorithm uses QR or LQ factorization of
otherwise. The algorithm uses QR or LQ factorization of  . It is assumed that
. It is assumed that  has full rank, infinity returned otherwise. Internally function uses
has full rank, infinity returned otherwise. Internally function uses ZGELS LAPACK routines. If 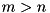 and
and transpose=false or 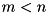 and
and transpose=true, then the system is overdetermined, thus the algorithm tries to find the least squares solution 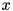 of the problem
of the problem
![\[ \|A*x-b\|_2\to\min\quad\text{or}\quad\|A^H*x-b\|_2\to\min\ \]](form_40.png)
respectively. Real number dErr (or vector vErr for multiple vector  case) returns residual sum of squares. The system is underdetermined otherwise, and the algorithm finds its minimum norm solution. In this case
case) returns residual sum of squares. The system is underdetermined otherwise, and the algorithm finds its minimum norm solution. In this case bErr is set to zero. In both cases the solution computed satisfies  , but this algorithm is faster than pseudo inversion. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
, but this algorithm is faster than pseudo inversion. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | conjugate | True to compute for conjugated matrix  (calling matrix). (calling matrix). |
| [in] | mA | cmatrix  . . |
| [in] | mB | cmatrix  . . |
| [out] | vErr | Norms of computation errors. |
Definition at line 21587 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Overdetermined or underdetermined linear solver.
Creates object of type cvector as a solution of overdetermined or underdetermined linear system
![\[ A*x=b \]](form_34.png)
for  complex matrix
complex matrix  (or conjugated one) where
(or conjugated one) where  is a vector of length
is a vector of length 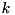 where
where 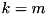 in non-transposed case and
in non-transposed case and 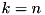 otherwise. The algorithm uses QR or LQ factorization of
otherwise. The algorithm uses QR or LQ factorization of  . It is assumed that
. It is assumed that  has full rank, infinity returned otherwise. Internally function uses
has full rank, infinity returned otherwise. Internally function uses ZGELS LAPACK routines. If 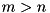 and
and transpose=false or 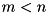 and
and transpose=true, then the system is overdetermined, thus the algorithm tries to find the least squares solution 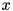 of the problem
of the problem
![\[ \|A*x-b\|_2\to\min\quad\text{or}\quad\|A^H*x-b\|_2\to\min\ \]](form_40.png)
respectively. Real number dErr returns residual sum of squares. The system is underdetermined otherwise, and the algorithm finds its minimum norm solution. In this case bErr is set to zero. In both cases the solution computed satisfies  , but this algorithm is faster than pseudo inversion. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
, but this algorithm is faster than pseudo inversion. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | conjugate | True to compute for conjugated matrix  (calling matrix). (calling matrix). |
| [in] | vB | cvector  . . |
| [out] | dErr | Norm of computation error. |
Definition at line 21664 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Linear least squares problem.
Function creates cmatrix object with the minimum-norm solutions to linear least squares problems
![\[ \|A*x-b\|_2\to\min \]](form_42.png)
using complete orthogonal factorization of  calling complex matrix
calling complex matrix  . Here
. Here  is a vector of length
is a vector of length 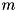 . Multiple vectors
. Multiple vectors  are stored as columns of
are stored as columns of 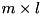 matrix
matrix  . Matrix
. Matrix  may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in
may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in rank output parameter using tol tolerance. Internally function uses ZGELSY LAPACK routines, see more details about the algorithm in those routines' documentation. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | mB | cmatrix  . . |
| [out] | rank | Rank of matrix  . . |
| [in] | tol | Rank computation tolerance. |
Definition at line 21732 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Linear least squares problem.
Function sets calling matrix to the minimum-norm solutions to linear least squares problems
![\[ \|A*x-b\|_2\to\min \]](form_42.png)
using complete orthogonal factorization of  complex matrix
complex matrix  (parameter
(parameter mA). Here  is a vector of length
is a vector of length 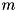 . Multiple vectors
. Multiple vectors  are stored as columns of
are stored as columns of 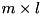 matrix
matrix  . Matrix
. Matrix  may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in
may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in rank output parameter using tol tolerance. Internally function uses ZGELSY LAPACK routines, see more details about the algorithm in those routines' documentation. Matrix  is passed as argument
is passed as argument mA. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | mA | cmatrix  . . |
| [in] | mB | cmatrix  . . |
| [out] | rank | Rank of matrix  . . |
| [in] | tol | Rank computation tolerance. |
Definition at line 21799 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Linear least squares problem.
Function creates cvector object with the minimum-norm solution to linear least squares problem
![\[ \|A*x-b\|_2\to\min \]](form_42.png)
using complete orthogonal factorization of  calling complex matrix
calling complex matrix  . Here
. Here  is a vector of length
is a vector of length 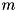 . Matrix
. Matrix  may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in
may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in rank output parameter using tol tolerance. Internally function uses ZGELSY LAPACK routines, see more details about the algorithm in those routines' documentation. Matrix  is passed as argument
is passed as argument mA. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | vB | cvector  . . |
| [out] | rank | Rank of matrix  . . |
| [in] | tol | Rank computation tolerance. |
Definition at line 21865 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Linear least squares problem.
Function creates cmatrix object with the minimum-norm solutions to linear least squares problems
![\[ \|A*x-b\|_2\to\min \]](form_42.png)
using singular value decomposition of  calling complex matrix
calling complex matrix  . Here
. Here  is a vector of length
is a vector of length 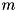 . Multiple vectors
. Multiple vectors  are stored as columns of
are stored as columns of 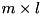 matrix
matrix  . Matrix
. Matrix  may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in
may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in rank output parameter using tol tolerance. Internally function uses ZGELSY LAPACK routines, see more details about the algorithm in those routines' documentation. Function also computes singular values of  in decreasing order and returns them in
in decreasing order and returns them in sv output parameter having 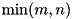 size. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
size. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | mB | cmatrix  . . |
| [out] | sv | Singular values of  . . |
| [out] | rank | Rank of matrix  . . |
| [in] | tol | Rank computation tolerance. |
|
inline |
Linear least squares problem.
Function sets calling matrix to the minimum-norm solutions to linear least squares problems
![\[ \|A*x-b\|_2\to\min \]](form_42.png)
using singular value decomposition of  complex matrix
complex matrix  (parameter
(parameter mA). Here  is a vector of length
is a vector of length 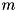 . Multiple vectors
. Multiple vectors  are stored as columns of
are stored as columns of 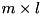 matrix
matrix  . Matrix
. Matrix  may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in
may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in rank output parameter using tol tolerance. Internally function uses ZGELSY LAPACK routines, see more details about the algorithm in those routines' documentation. Matrix  is passed as argument
is passed as argument mA. Function also computes singular values of  in decreasing order and returns them in
in decreasing order and returns them in sv output parameter having 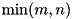 size. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
size. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | mA | cmatrix  . . |
| [in] | mB | cmatrix  . . |
| [out] | sv | Singular values of  . . |
| [out] | rank | Rank of matrix  . . |
| [in] | tol | Rank computation tolerance. |
|
inline |
Linear least squares problem.
Function creates cvector object with the minimum-norm solution to linear least squares problem
![\[ \|A*x-b\|_2\to\min \]](form_42.png)
using singular value decomposition of  calling complex matrix
calling complex matrix  . Here
. Here  is a vector of length
is a vector of length 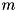 . Matrix
. Matrix  may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in
may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in rank output parameter using tol tolerance. Internally function uses ZGELSY LAPACK routines, see more details about the algorithm in those routines' documentation. Matrix  is passed as argument
is passed as argument mA. Function also computes singular values of  in decreasing order and returns them in
in decreasing order and returns them in sv output parameter having 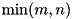 size. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
size. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | vB | cvector  . . |
| [out] | sv | Singular values of  . . |
| [out] | rank | Rank of matrix  . . |
| [in] | tol | Rank computation tolerance. |
|
inline |
Linear least squares problem.
Function creates cmatrix object with the minimum-norm solutions to linear least squares problems
![\[ \|A*x-b\|_2\to\min \]](form_42.png)
using singular value decomposition of  calling complex matrix
calling complex matrix  and divide and conquer method. Here
and divide and conquer method. Here  is a vector of length
is a vector of length 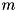 . Multiple vectors
. Multiple vectors  are stored as columns of
are stored as columns of 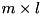 matrix
matrix  . Matrix
. Matrix  may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in
may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in rank output parameter using tol tolerance. Internally function uses ZGELSY LAPACK routines, see more details about the algorithm in those routines' documentation. Function also computes singular values of  in decreasing order and returns them in
in decreasing order and returns them in sv output parameter having 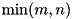 size. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
size. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | mB | cmatrix  . . |
| [out] | sv | Singular values of  . . |
| [out] | rank | Rank of matrix  . . |
| [in] | tol | Rank computation tolerance. |
|
inline |
Linear least squares problem.
Function sets calling complex matrix to the minimum-norm solutions to linear least squares problems
![\[ \|A*x-b\|_2\to\min \]](form_42.png)
using singular value decomposition of  complex matrix
complex matrix  (parameter
(parameter mA) and divide and conquer method. Here  is a vector of length
is a vector of length 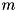 . Multiple vectors
. Multiple vectors  are stored as columns of
are stored as columns of 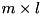 matrix
matrix  . Matrix
. Matrix  may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in
may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in rank output parameter using tol tolerance. Internally function uses ZGELSY LAPACK routines, see more details about the algorithm in those routines' documentation. Matrix  is passed as argument
is passed as argument mA. Function also computes singular values of  in decreasing order and returns them in
in decreasing order and returns them in sv output parameter having 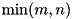 size. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
size. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | mA | cmatrix  . . |
| [in] | mB | cmatrix  . . |
| [out] | sv | Singular values of  . . |
| [out] | rank | Rank of matrix  . . |
| [in] | tol | Rank computation tolerance. |
|
inline |
Linear least squares problem.
Function creates cvector object with the minimum-norm solution to linear least squares problem
![\[ \|A*x-b\|_2\to\min \]](form_42.png)
using singular value decomposition of  calling complex matrix
calling complex matrix  and divide and conquer method. Here
and divide and conquer method. Here  is a vector of length
is a vector of length 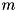 . Matrix
. Matrix  may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in
may be rank-deficient, function returns its effective rank in rank output parameter using tol tolerance. Internally function uses ZGELSY LAPACK routines, see more details about the algorithm in those routines' documentation. Matrix  is passed as argument
is passed as argument mA. Function also computes singular values of  in decreasing order and returns them in
in decreasing order and returns them in sv output parameter having 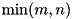 size. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
size. It throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands.
| [in] | vB | cvector  . . |
| [out] | sv | Singular values of  . . |
| [out] | rank | Rank of matrix  . . |
| [in] | tol | Rank computation tolerance. |
|
inline |
Matrix rank.
Returns rank of calling complex matrix as number of singular values with normalized absolute value greater than or equal to parameter tol (this is the largest relative spacing by default). Function throws cvmexception in case of convergence error.
| [in] | tol | Rank computation tolerance. |
Definition at line 22316 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
QR factorization ("economy" mode)
Computes QR factorization as
![\[ M=QR \]](form_89.png)
where  is calling matrix, orthogonal matrix
is calling matrix, orthogonal matrix  and upper triangular (trapezoidal) matrix
and upper triangular (trapezoidal) matrix  are
are mQ and mR output parameters respectively. This version implements so-called "economy" algorithm which for given  matrix
matrix  computes
computes  matrix
matrix  and
and 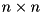 matrix
matrix 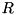 . See also full version. Function throws cvmexception in case if inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
. See also full version. Function throws cvmexception in case if inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
|
inline |
QR factorization ("full" mode)
Computes QR factorization as
![\[ M=QR \]](form_89.png)
where  is calling matrix, orthogonal matrix
is calling matrix, orthogonal matrix 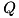 and upper triangular (trapezoidal) matrix
and upper triangular (trapezoidal) matrix 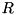 are
are mQ and mR output parameters respectively. This version implements so-called "full" algorithm which for given  matrix
matrix  computes
computes 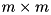 matrix
matrix 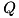 and
and  matrix
matrix 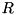 . See also economy version. Function throws cvmexception in case if inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
. See also economy version. Function throws cvmexception in case if inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
|
inline |
LQ factorization ("economy" mode)
Computes LQ factorization as
![\[ M=LQ \]](form_91.png)
where  is calling matrix, lower triangular (trapezoidal) matrix
is calling matrix, lower triangular (trapezoidal) matrix 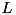 and orthogonal matrix
and orthogonal matrix 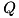 are
are mL and mQ output parameters respectively. This version implements so-called "economy" algorithm which for given  matrix
matrix  computes
computes 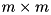 matrix
matrix 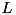 and
and  matrix
matrix 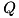 . See also full version. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
. See also full version. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
|
inline |
LQ factorization ("full" mode)
Computes LQ factorization as
![\[ M=LQ \]](form_91.png)
where  is calling matrix, lower triangular (trapezoidal) matrix
is calling matrix, lower triangular (trapezoidal) matrix 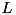 and orthogonal matrix
and orthogonal matrix 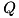 are
are mL and mQ output parameters respectively. This version implements so-called "full" algorithm which for given  matrix
matrix  computes
computes  matrix
matrix 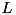 and
and 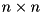 matrix
matrix 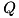 . See also economy version. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
. See also economy version. Function throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
|
inline |
RQ factorization ("economy" mode)
Computes RQ factorization as
![\[ M=RQ \]](form_93.png)
where  is calling matrix, upper triangular matrix
is calling matrix, upper triangular matrix 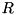 and orthogonal matrix
and orthogonal matrix 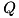 are
are mR and mQ output parameters respectively. This version implements so-called "economy" algorithm which for given  matrix
matrix  computes
computes 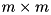 matrix
matrix 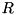 and
and  matrix
matrix 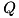 . See also full version. Following this definition the implementation assumes that
. See also full version. Following this definition the implementation assumes that 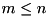 is satisfied and throws cvmexception otherwise. Function also throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
is satisfied and throws cvmexception otherwise. Function also throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
|
inline |
RQ factorization ("full" mode)
Computes RQ factorization as
![\[ M=RQ \]](form_93.png)
where  is calling matrix, upper triangular matrix
is calling matrix, upper triangular matrix 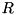 and orthogonal matrix
and orthogonal matrix 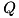 are
are mR and mQ output parameters respectively. This version implements so-called "full" algorithm which for given  matrix
matrix  computes
computes  matrix
matrix 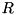 and
and  matrix
matrix  . See also economy version. Following this definition the implementation assumes that
. See also economy version. Following this definition the implementation assumes that 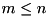 is satisfied and throws cvmexception otherwise. Function also throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
is satisfied and throws cvmexception otherwise. Function also throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
|
inline |
QL factorization ("economy" mode)
Computes QL factorization as
![\[ M=QL \]](form_95.png)
where  is calling matrix, orthogonal matrix
is calling matrix, orthogonal matrix  and lower triangular matrix
and lower triangular matrix 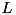 are
are mQ and mL output parameters respectively. This version implements so-called "economy" algorithm which for given  matrix
matrix  computes
computes  matrix
matrix  and
and 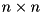 matrix
matrix 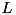 . See also full version. Following this definition the implementation assumes that
. See also full version. Following this definition the implementation assumes that  is satisfied and throws cvmexception otherwise. Function also throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
is satisfied and throws cvmexception otherwise. Function also throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
|
inline |
QL factorization ("full" mode)
Computes QL factorization as
![\[ M=QL \]](form_95.png)
where  is calling matrix, orthogonal matrix
is calling matrix, orthogonal matrix 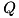 and lower triangular matrix
and lower triangular matrix 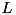 are
are mQ and mL output parameters respectively. This version implements so-called "full" algorithm which for given  matrix
matrix  computes
computes 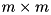 matrix
matrix 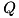 and
and  matrix
matrix 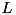 . See also economy version. Following this definition the implementation assumes that
. See also economy version. Following this definition the implementation assumes that  is satisfied and throws cvmexception otherwise. Function also throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
is satisfied and throws cvmexception otherwise. Function also throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands passed.
|
inline |
Rank-1 update matrix-vector operation (unconjugated)
Calls one of ZGER routines of the BLAS library performing rank-1 update matrix-vector operation defined as
![\[ M=\alpha\,\begin{pmatrix} x_1 \\ x_2 \\ \vdots \\ x_m \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} y_1 & y_2 & \cdots & y_n \end{pmatrix} + M, \]](form_97.png)
where 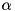 is complex number (parameter
is complex number (parameter dAlpha),  is calling matrix and
is calling matrix and 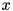 and
and 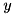 are complex vectors (parameters
are complex vectors (parameters vCol and vRow respectively). Function returns reference to the matrix changed and throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands. Function is not applicable to objects of the classes scbmatrix and schmatrix (i.e. cvmexception would be thrown).
Definition at line 22773 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Rank-1 update matrix-vector operation (conjugated)
Calls one of ZGER routines of the BLAS library performing rank-1 update matrix-vector operation defined as
![\[ M=\alpha\,\begin{pmatrix} x_1 \\ x_2 \\ \vdots \\ x_m \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} y_1^* & y_2^* & \cdots & y_n^* \end{pmatrix} + M, \]](form_129.png)
where 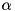 is complex number (parameter
is complex number (parameter dAlpha),  is calling matrix and
is calling matrix and 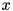 and
and 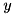 are complex vectors (parameters
are complex vectors (parameters vCol and vRow respectively). Function returns reference to the matrix changed and throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands. Function is not applicable to objects of the classes scbmatrix and schmatrix (i.e. cvmexception would be thrown).
Definition at line 22839 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Generic matrix-matrix operation.
Calls one of ZGEMM routines of the BLAS library performing matrix-matrix operation defined as
![\[ M=\alpha\,\mathcal{T}(M_1)\cdot\mathcal{T}(M_2) + \beta M, \]](form_98.png)
where 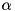 and
and 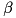 are complex numbers (parameters
are complex numbers (parameters dAlpha and dBeta),  is calling matrix and
is calling matrix and 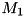 and
and 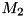 are matrices (parameters
are matrices (parameters m1 and m2 respectively). Function  conjugatess matrix
conjugatess matrix  if appropriate boolean parameter
if appropriate boolean parameter bConj* is equal to true and does nothing otherwise. Function returns reference to the matrix changed and throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands. Function is not applicable to objects of the classes srbmatrix and srsmatrix (i.e. exception of type cvmexception would be thrown).
| [in] | m1 | cmatrix 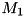 . . |
| [in] | bConj1 | Conjugate cmatrix 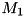 . . |
| [in] | m2 | cmatrix 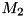 . . |
| [in] | bConj2 | Conjugate cmatrix 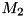 . . |
| [in] | cAlpha | Multiplier 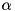 . . |
| [in] | cBeta | Multiplier  . . |
Definition at line 22908 of file cvm.h.
|
inline |
Generic hermitian matrix-matrix operation.
Calls one of ZHEMM routines of the BLAS library performing one of matrix-matrix operations defined as
![\[ M=\alpha\,M_s\cdot M_1 + \beta M\quad\text{or}\quad M=\alpha\,M_1\cdot M_s + \beta M, \]](form_103.png)
where  and
and 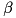 are complex numbers (parameters
are complex numbers (parameters cAlpha and cBeta),  is calling matrix,
is calling matrix, 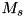 is hermitian matrix and
is hermitian matrix and 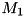 is complex matrix (parameters
is complex matrix (parameters ms and m respectively). First operation is performed if bLeft passed is true and second one otherwise. Function returns reference to the matrix changed and throws cvmexception in case of inappropriate sizes of the operands. Function is not applicable to objects of the class scbmatrix (i.e. cvmexception would be thrown).
| [in] | bLeft | Perfoem left-side operation. |
| [in] | ms | schmatrix 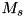 . . |
| [in] | m | cmatrix 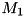 . . |
| [in] | cAlpha | Multiplier 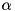 . . |
| [in] | cBeta | Multiplier 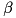 . . |
Definition at line 22990 of file cvm.h.

|
inline |
Set matrix to zero.
Sets every element of calling matrix to be equal to zero and returns reference to the matrix changed. This function is faster than, for example, set(TC) with zero parameter passed.
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Randomizer (real part)
Fills real part of calling complex matrix with pseudo-random numbers distributed between dFrom and dTo. It returns reference to the matrix changed.
| [in] | dFrom | First limit. |
| [in] | dTo | Second limit. |
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inline |
Randomizer (imaginary part)
Fills imaginary part of calling complex matrix with pseudo-random numbers distributed between dFrom and dTo. It returns reference to the matrix changed.
| [in] | dFrom | First limit. |
| [in] | dTo | Second limit. |
Reimplemented in basic_schmatrix< TR, TC >, basic_scbmatrix< TR, TC >, and basic_scmatrix< TR, TC >.
|
inlineoverridevirtual |
2-norm
2-norm of calling array that for vectors is defined as
![\[ {\|x\|}_2={\|x\|}_E=\left(\sum_{i=1}^{n} |x_i|^2\right)^{1/2} \]](form_20.png)
and for matrices as
![\[ {\|A\|}_2=\max_i\sigma_i = \left(\max_{|x|=1}\, (Ax\cdot Ax)\right)^{1/2}, \]](form_21.png)
where  is
is 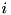 -th singular value of
-th singular value of  matrix
matrix 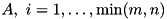 .
.
Reimplemented from basic_array< TR, TC >.
Definition at line 23095 of file cvm.h.

|
friend |
 1.8.1.2
1.8.1.2